Google Cloud Identity
Cloud Identity is Google’s identity and access management (IAM) solution. Cloud Identity is the backbone of Google Workspace (formerly Google Apps for Business or G Suite).
So Cloud Identity is the counterpart from Google to Microsoft’s Azure AD.
Cloud Identity is an Identity as a Service (IDaaS) and enterprise mobility management (EMM) product. It offers the identity services and endpoint administration that are available in Google Workspace as a stand-alone product. As an administrator, you can use Cloud Identity to manage your users, apps, and devices from a central location—the Google Admin console.
Source: https://support.google.com/cloudidentity/answer/7319251?hl=en
Key Features
- Give users easy access to apps with single sign-on
- Multi-factor authentication protects user and company data
- Endpoint management enforces policies for personal and corporate devices
Source: https://cloud.google.com/identity#section-2
When you create an Google Workspace account, out of the box Cloud Identity is included.
This is like in Microsoft when you create an Office 365 account (rebranded in Microsoft 365 with further products and features like the Windows OS included) there is also an Azure AD provisioned with, which is the backbone of Microsoft 365 (Office 365) .
Google Workspace on the other hand is like Office 365 a collection of productivity and colaboration tools. It consists of Gmail, Contacts, Calendar, Meet and Chat for communication, Currents for employee engagement, Drive for storage and the Google Docs Editors suite for content creation.
The Cloud Identity directory service offers several APIs like a REST-API and Secure LDAP. Therefore you can migrate your on-premise applications which depends on LDAP also into the Google Cloud.
As already mentioned, Cloud Identity is also as standalone product available and you don’t need to setup Google Workspace to use it. There are two Cloud Identity Editions available:
- Cloud Identity Free edition includes core identity and endpoint management services. It provides managed Google Accounts to users who don’t need certain Google Workspace services, such as Gmail and Google Calendar. However, users can access Google Drive, Docs, Sheets, Slides, Keep, and Meet. You can use Cloud Identity accounts with other Google services, such as Google Cloud, Chrome, Android enterprise, and many third-party applications. For more features, upgrade to Cloud Identity Premium edition.
- Cloud Identity Premium edition offers all of the features of the Free edition, plus enterprise security, application management, and device management services. These services include features such as automated user provisioning, app whitelisting, and automated mobile device management. Get started!
Google Workspace licenses are required only for users who need certain Google Workspace services, like Gmail. To manage users who don’t need any Google Workspace services, you can create free Cloud Identity accounts for them.
In most cases, Cloud Identity Free edition users have the same identity services as Google Workspace users, such as single sign-on (SSO) and 2-Step Verification (2SV).
Source: https://support.google.com/cloudidentity/answer/7319251?hl=en
To manage Cloud Identity you can use either use the Admin Console or the GCP Console.
The main functionality in Cloud Identity is to create users and groups for authentication and authorization in the Google Cloud.
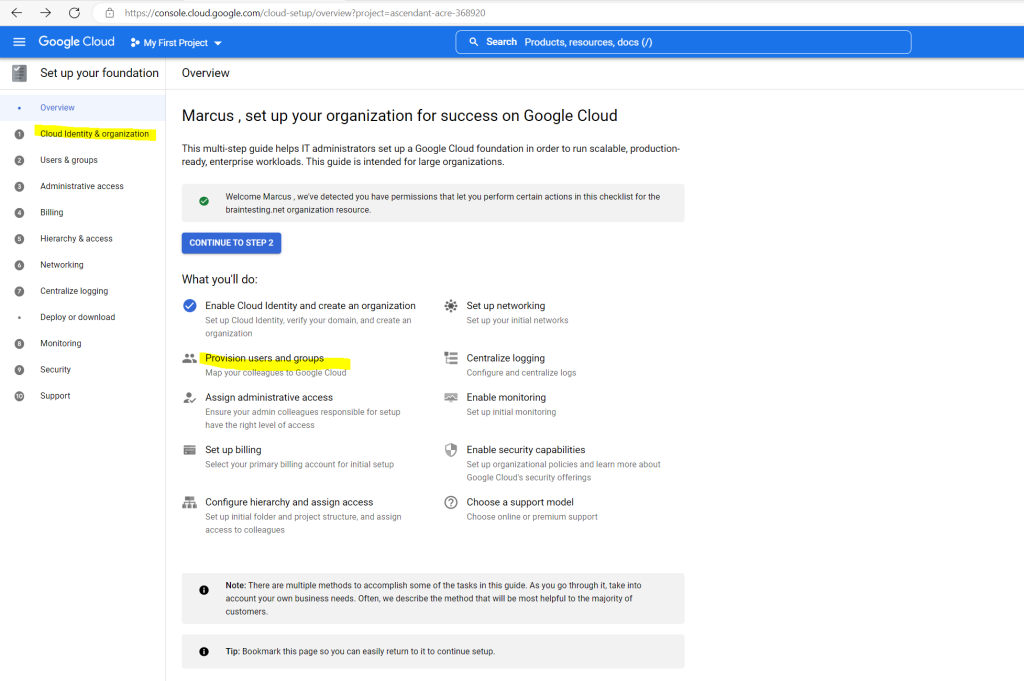
When you click in the GCP console on Cloud Identity & organization, you will get to the checklist to complete the tasks for the Google Cloud foundation.
Below in the screenshot you can see the first task with Enable Cloud Identity and create an organization is still completed for my account.
This completion of this task you can read in my following post.
As mentioned the main functionality of Cloud Identity is to create users and groups for authentication and authorization in the Google Cloud.
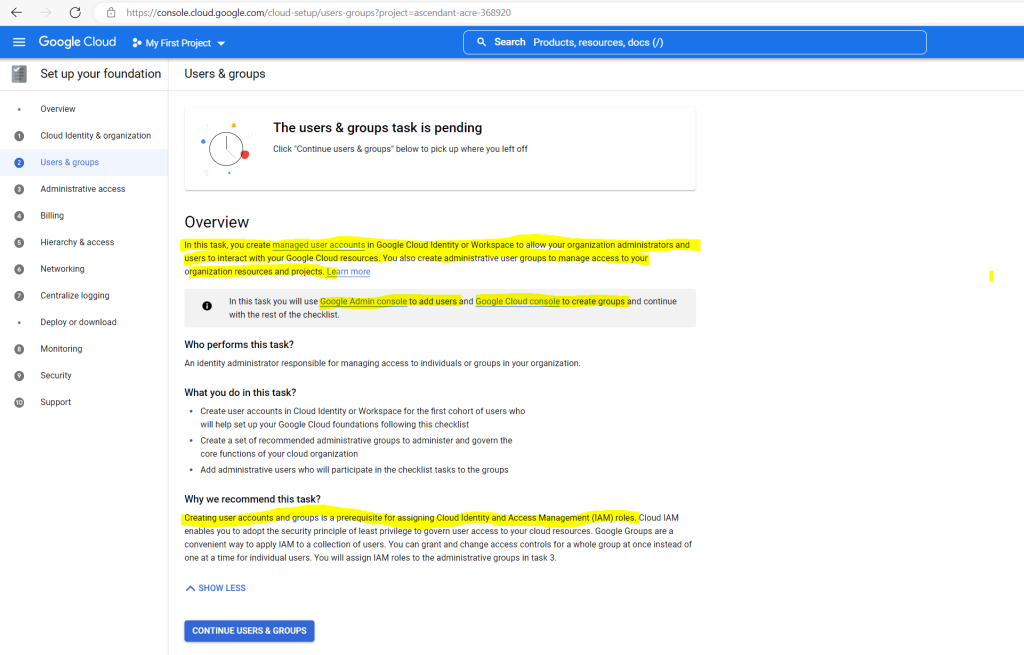
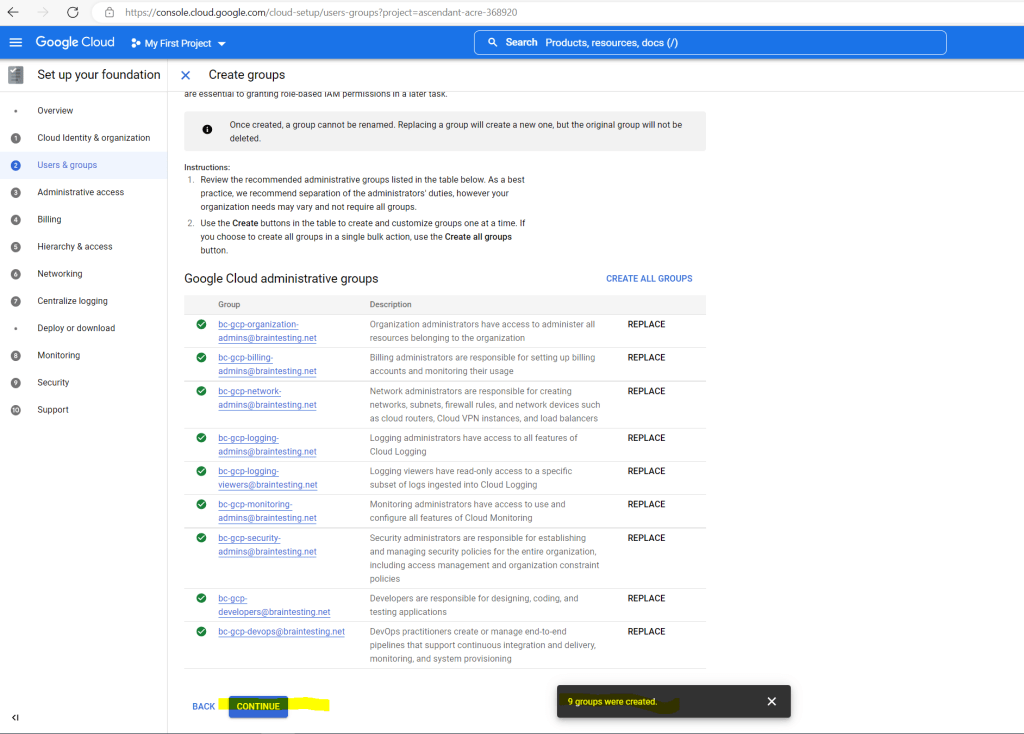
One of the tasks to set up the organization for Google Cloud is to provision users and groups as shown below in task 2.
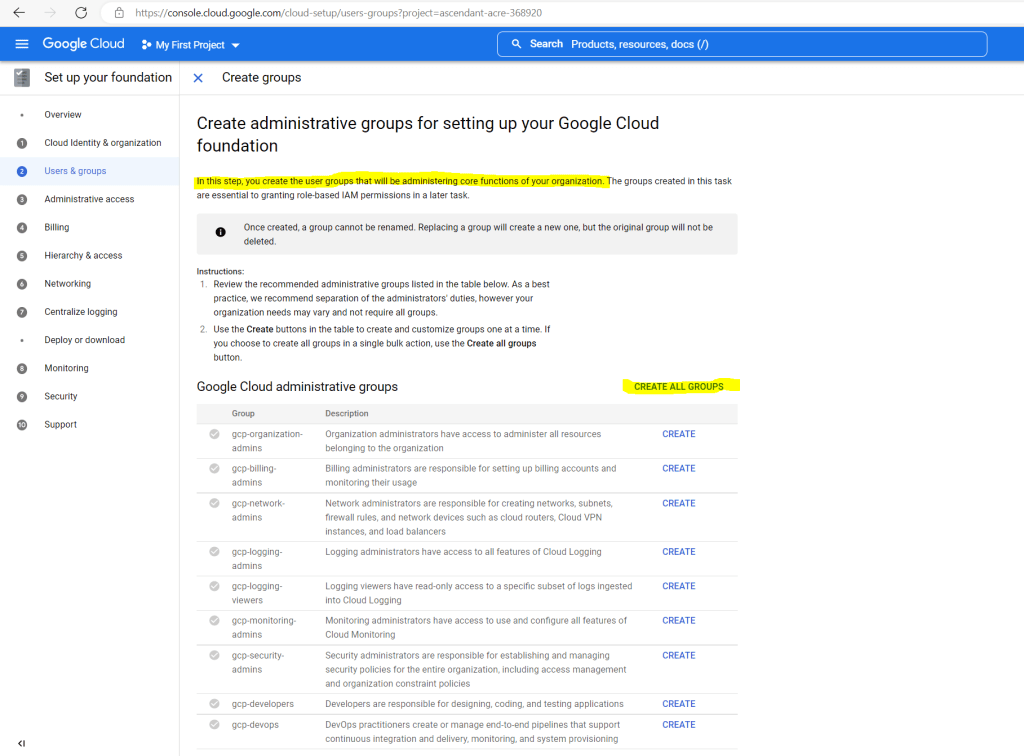
First by working on the checklist you can create the groups in Cloud Identity. For my lab-environment I will create all predefined groups.
I will also use a prefix to name the groups.
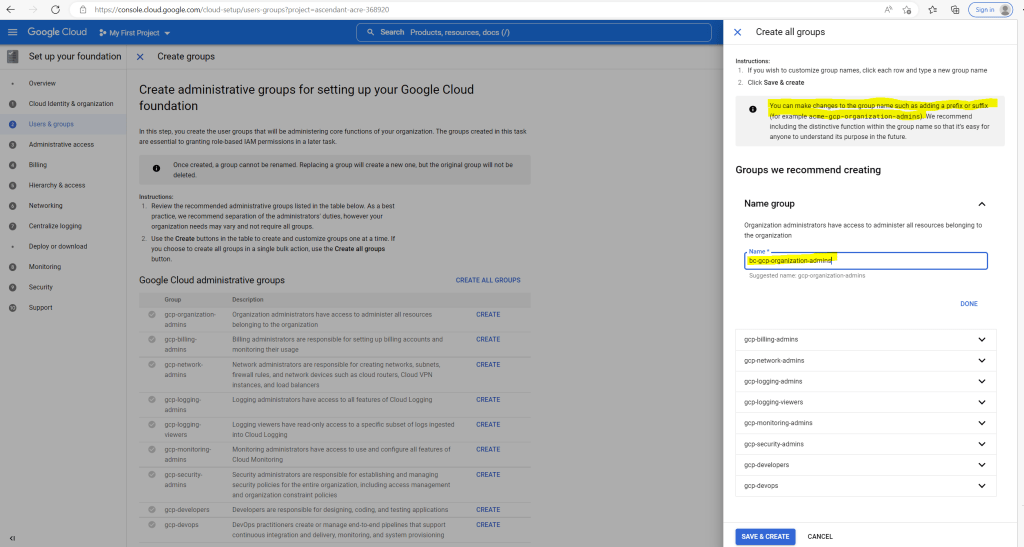
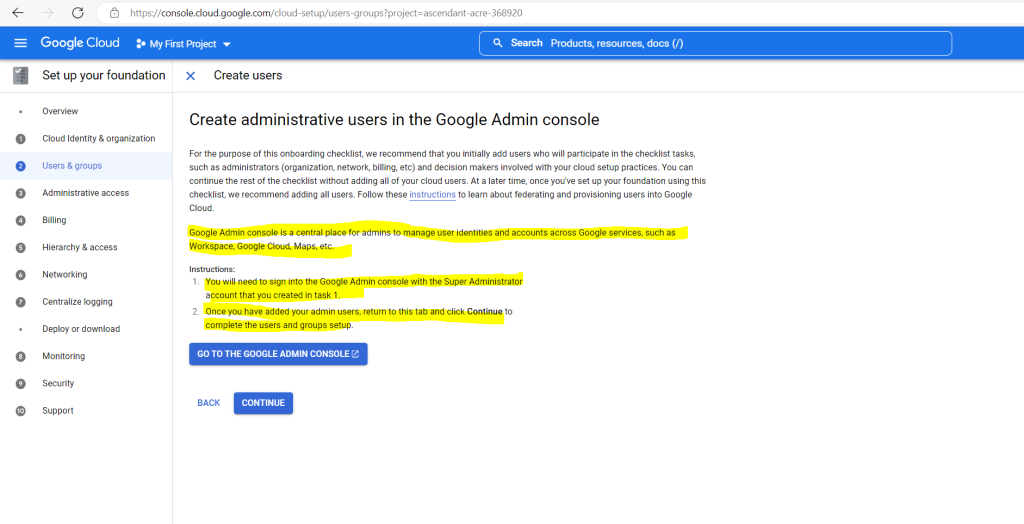
Below you can add further administrative users besides your super admin account.
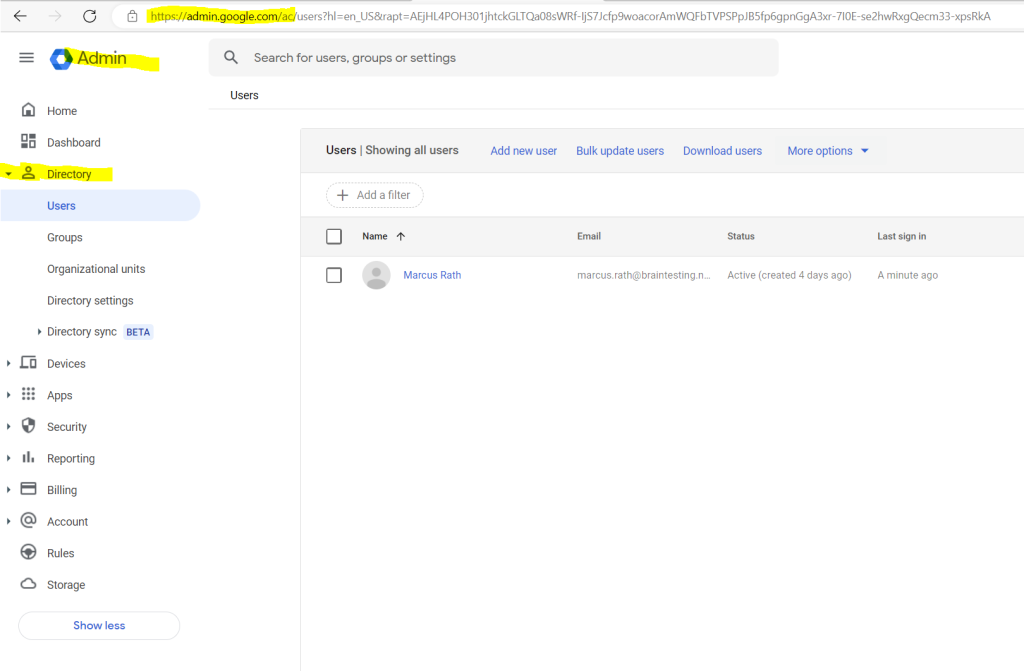
So to create further administrative users I will get routed to the Admin Console and the Directory – Users menu as shown below.
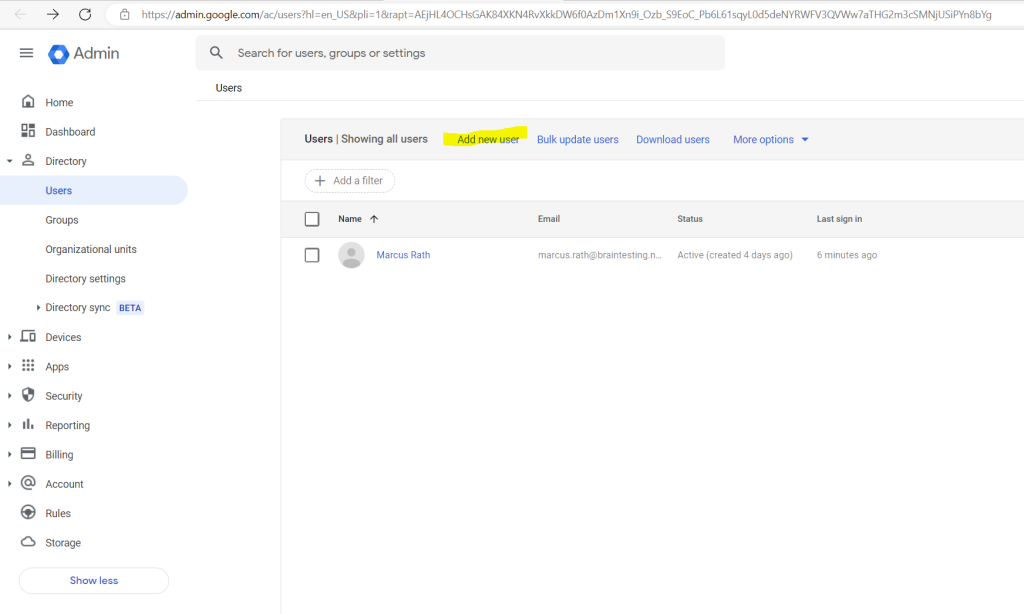
Below I will create a new user in the Admin Console.
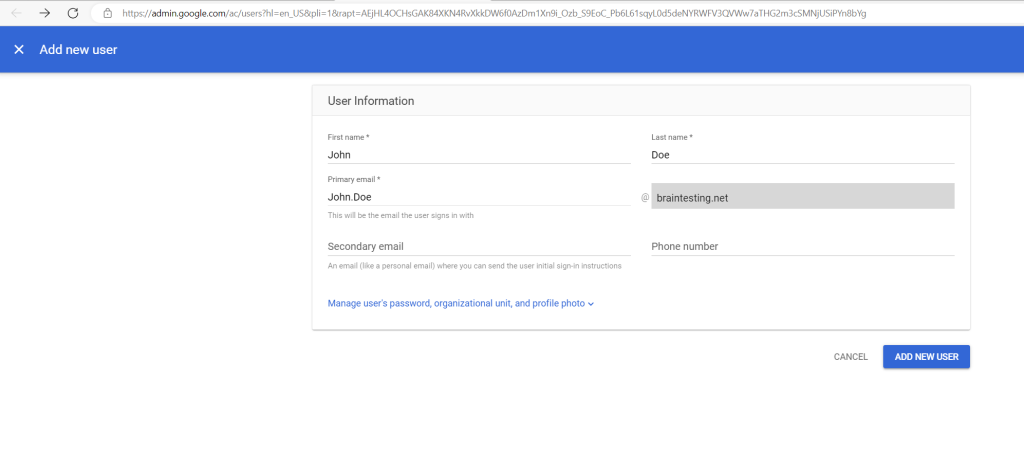
Below you can copy the initial password or send an email to the user containing the sign in instructions.
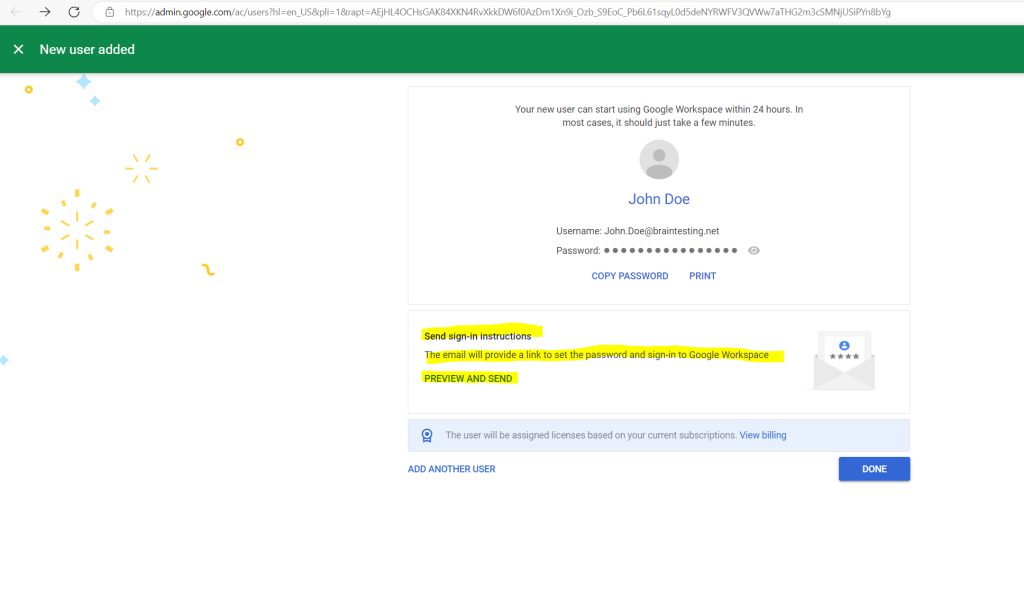
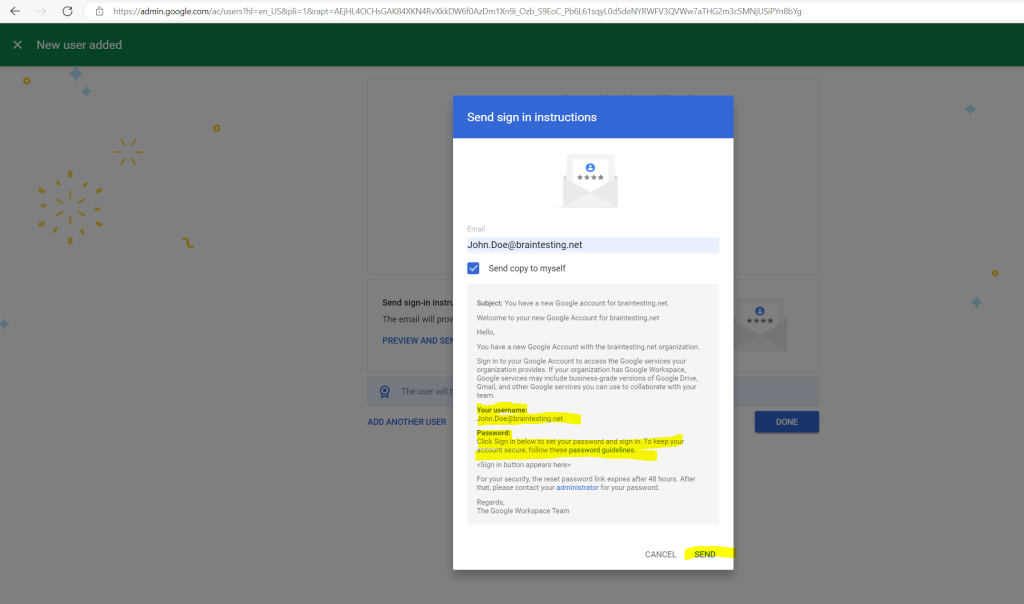
My user John Doe then will get the following mail from Google Cloud to its inbox.
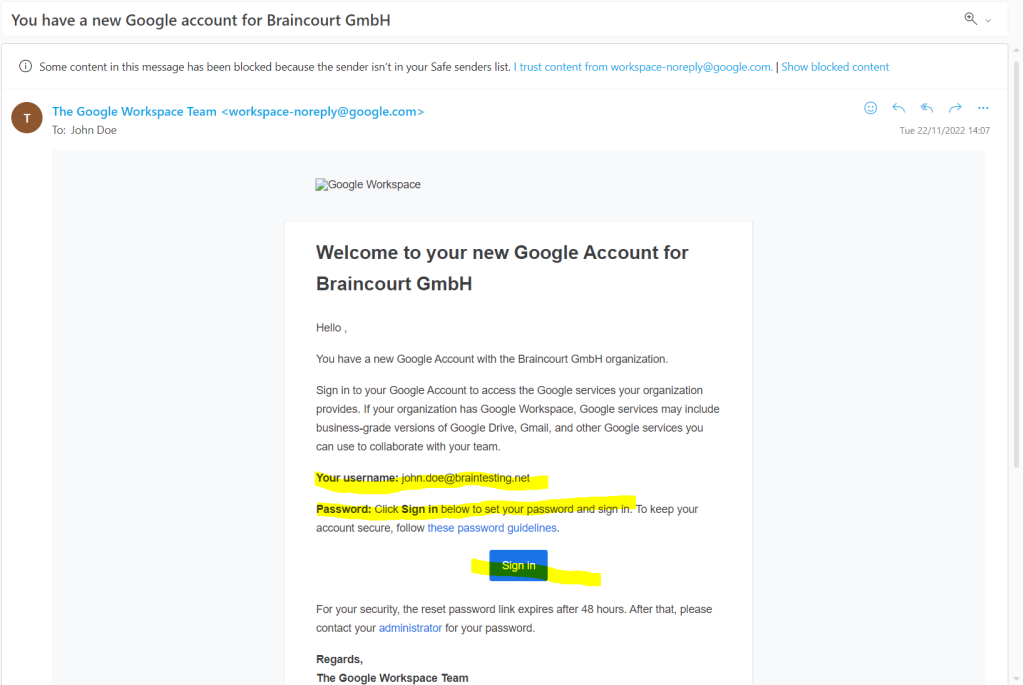
By clicking on the provided link above in its inbox, the user will get send to the follwing page.
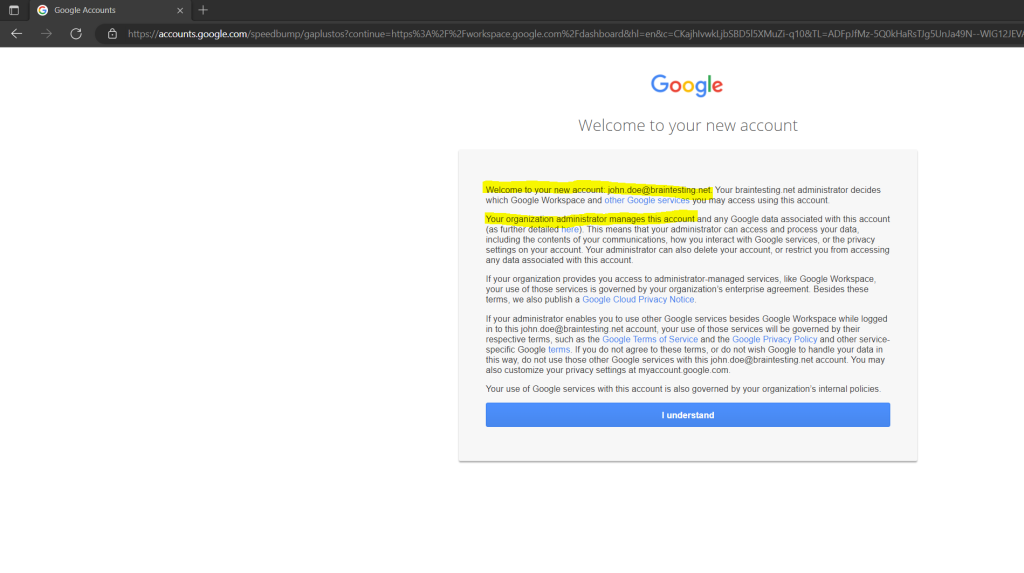
At first sign in the user must change the password.
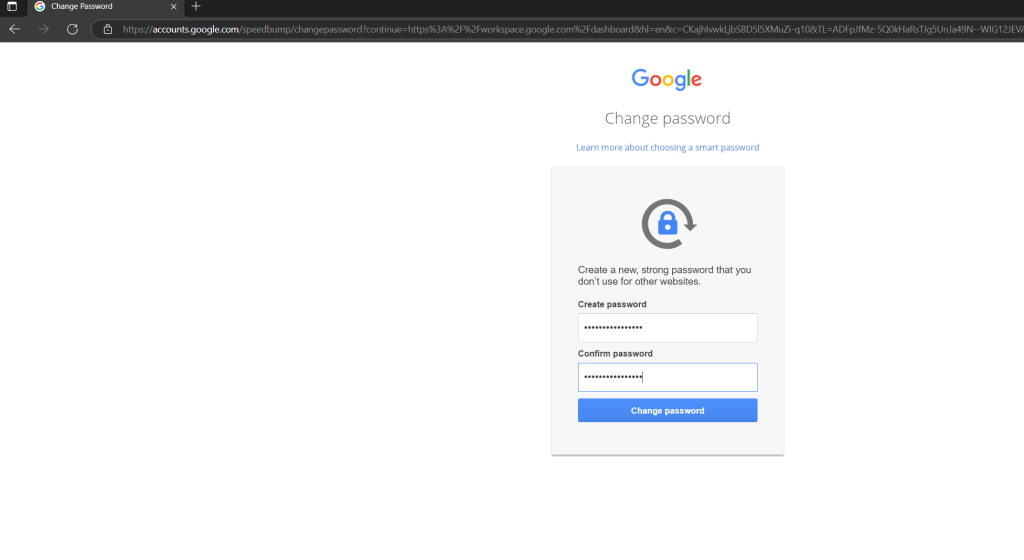
After sign in to your new Google Account you will get automatically redirected to the Google Workspace URL, even if the user hadn’t assigned any workspace licenses.
The business apps are missing without a license.
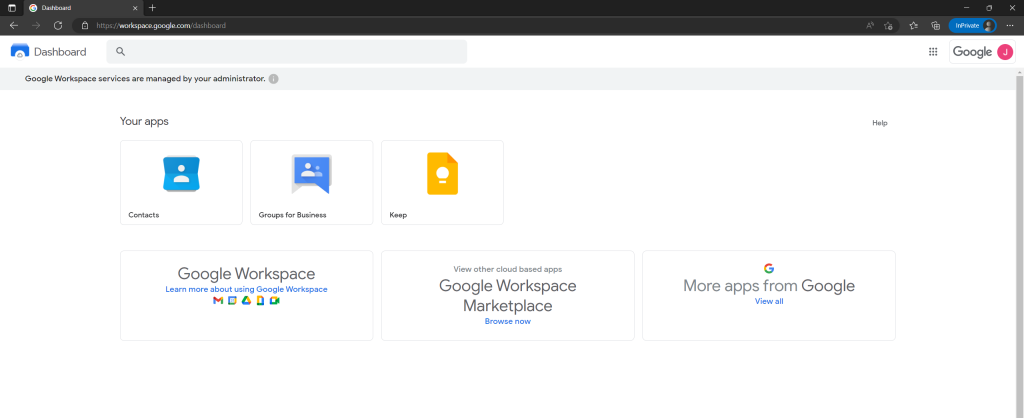
This is the same as in Microsoft 365, here Azure AD users they had no licenses assigned to can also sign in to Microsoft 365 and Azure, but cannot access and see the available apps as shown below.
To show the differences when a user had assigned a license, I will add a Google Workspace Business Starter license to the Google account from John Doe.
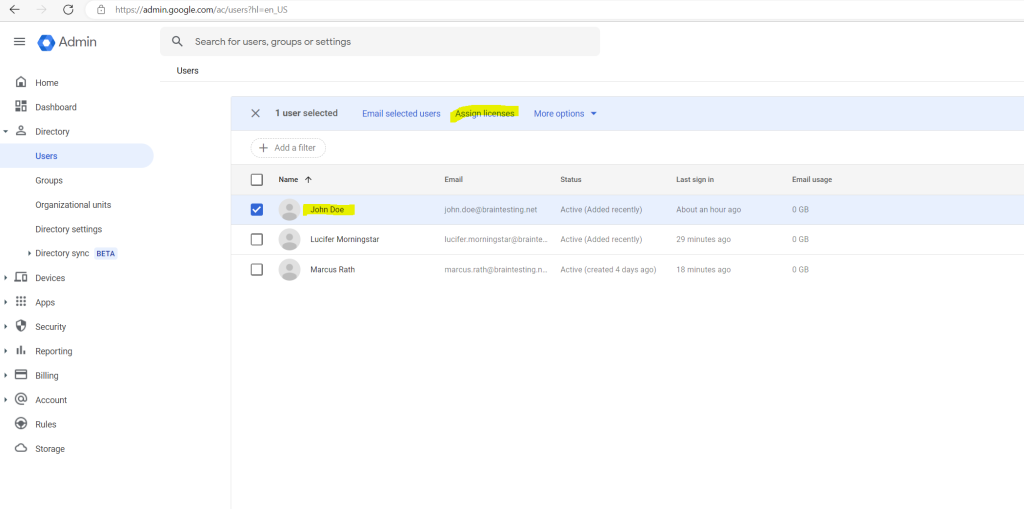
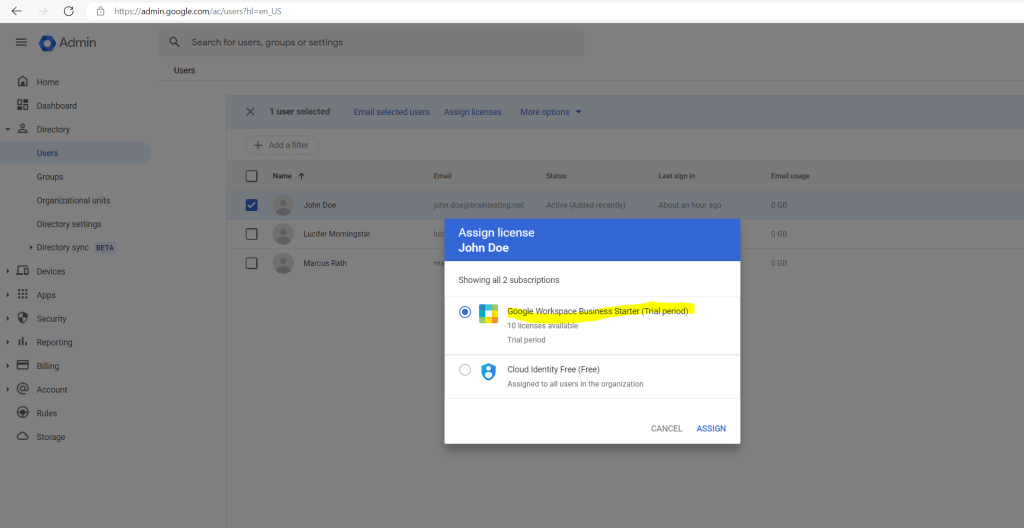
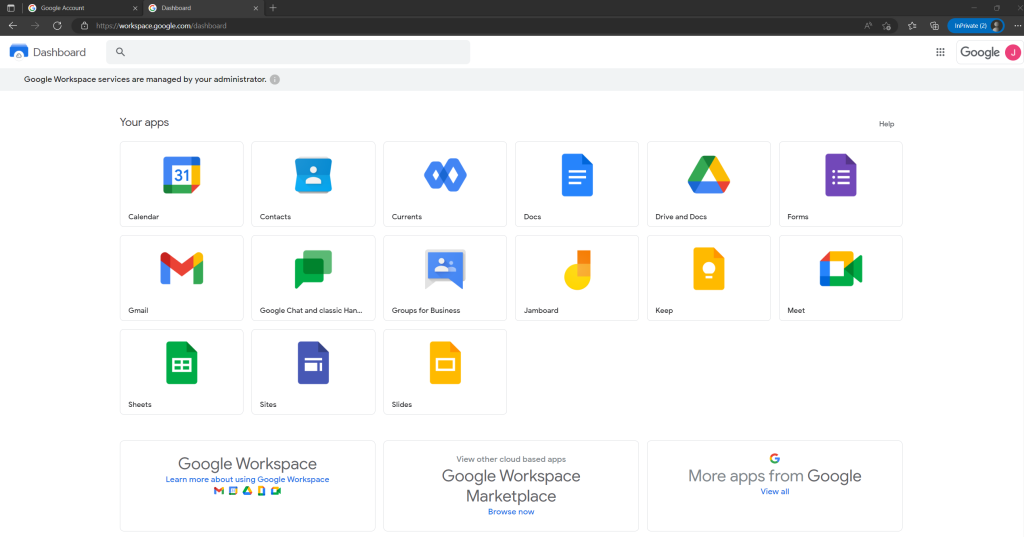
Now after assigning the Google Workspace Business Starter license, the user John Doe had new tools and apps like Gmail, Drive, Calendar and Meet video conferencing.
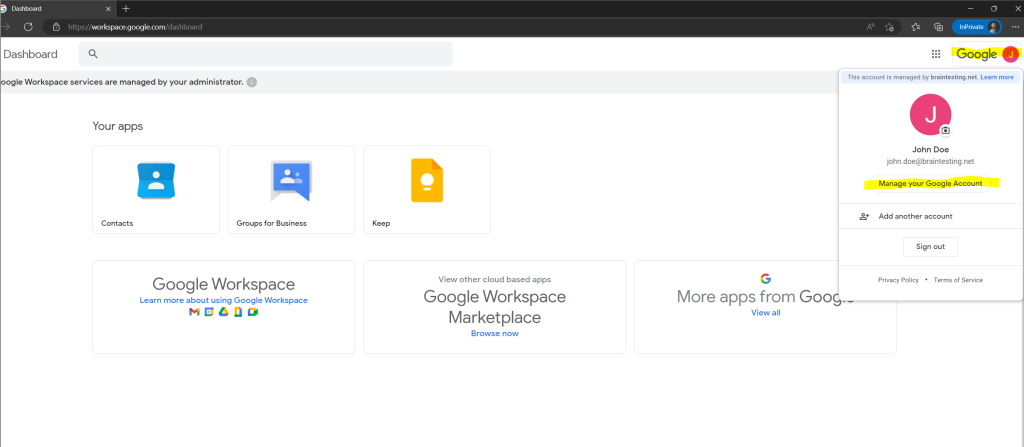
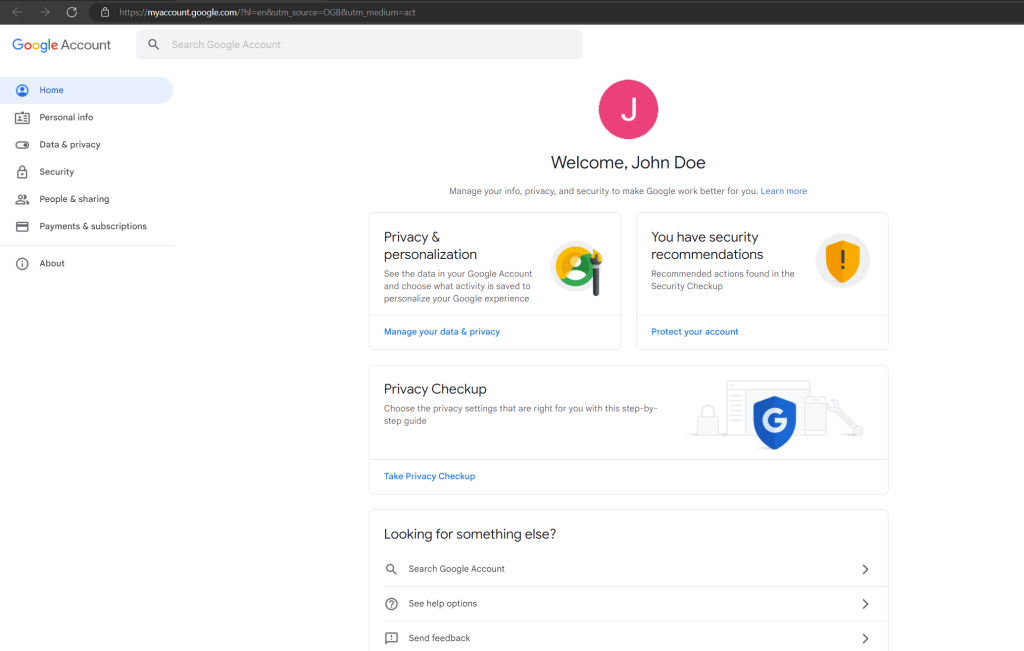
The user can also manage its account by clicking on the right top on the user icon and Manage your Google Account.
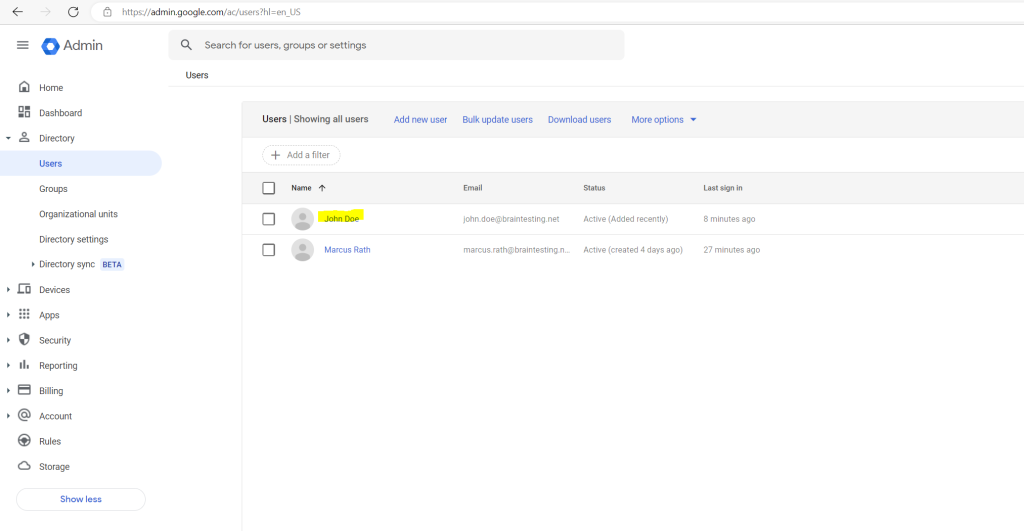
In the Admin Console under Users my new user is now listed.
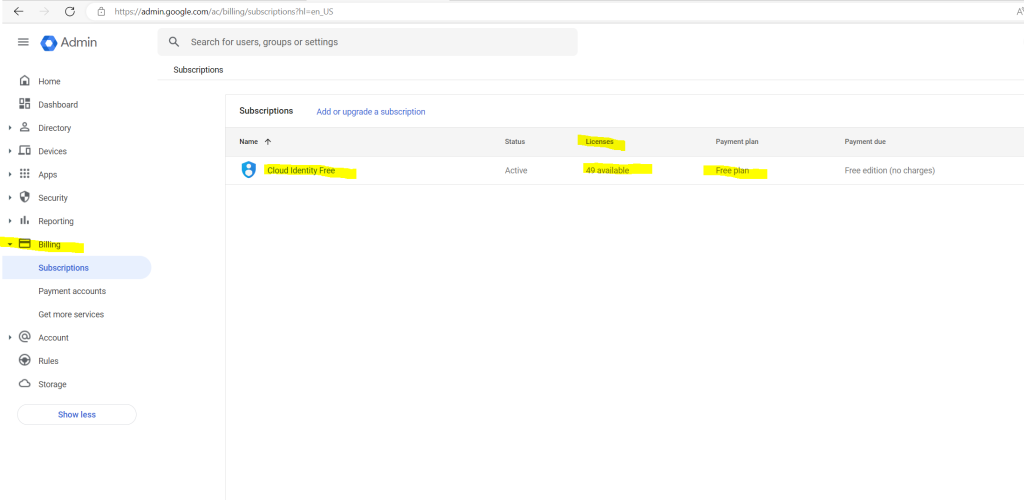
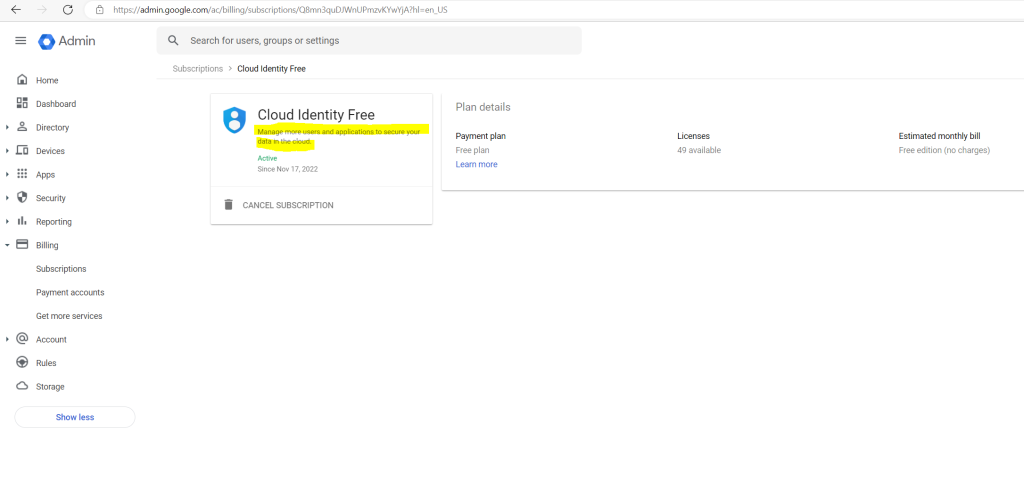
So far the only subscription I had in my lab environment is Cloud Identity Free where I can manage up to 50 users.
Links
Overview of Google identity management
https://cloud.google.com/architecture/identity/overview-google-authentication?hl=en-us
Tags In
Follow me on LinkedIn


