Set up a VMware vSphere Environment – Part 1
The main aim of this post is to give you a comprehensive guide and introduction about VMware’s vSphere environment.
In this first part we will see how to deploy the vCenter server appliance (VCSA) on an ESXi host in our on-premise data center.
Up to vSphere version 6.7 you could also install the vCenter Server on Windows but has been deprecated in versions after vSphere 6.7.
In part 2 we will then see how to configure this vCenter server appliance to finally set up and run our vSphere environment.
VMware vSphere is a comprehensive virtualization and cloud computing platform developed by VMware, Inc.
Finally vSphere is just the brand name and umbrella term for VMware’s suite of virtualization products and features, basically the ESXi hypervisor and vCenter Server.
vSphere provides a suite of virtualization products that enable organizations to create and manage virtualized IT infrastructures. The vSphere environment is designed to enhance the efficiency, flexibility, and scalability of data centers, allowing businesses to optimize their resources and streamline IT operations.
While vSphere itself is not a public cloud service, it serves as the foundation for building private and hybrid cloud environments. Organizations can leverage vSphere to create their own cloud infrastructure, providing the essential characteristics of cloud computing within their own data centers.
More about VMware’s cloud strategy including its cloud foundation which is a unified SDDC platform for private and public clouds you will find in the following article.
Cloud Computing
https://www.vmware.com/content/vmware/vmware-published-sites/de/solutions/cloud-computing.htmlSoftware Defined Data Center (SDDC) vs. Private Cloud
https://blog.matrixpost.net/software-defined-data-center-sddc-vs-private-cloud/
Introduction
The two core components of vSphere are ESXi and vCenter Server.
ESXi is the virtualization platform (hypervisor) on which you can create and run virtual machines and virtual appliances.
About how to set up and configure a VMware ESXi Host you can read my following post.
vCenter server is a service that acts as a central administrator for ESXi hosts connected in a network. vCenter Server lets you pool and manage the resources of multiple hosts.
You deploy the vCenter Server appliance, a preconfigured virtual machine optimized for running vCenter Server and the vCenter Server components. You can deploy the vCenter Server appliance on ESXi hosts or on vCenter Server instances.
The vCenter server is similar like Microsoft’s Virtual Machine Manger (VMM).
Set up a VMware vSphere environment
vSphere is a sophisticated product with multiple components to install and set up. To ensure a successful vSphere deployment, understand the sequence of tasks required.
Installing vSphere includes the following tasks:
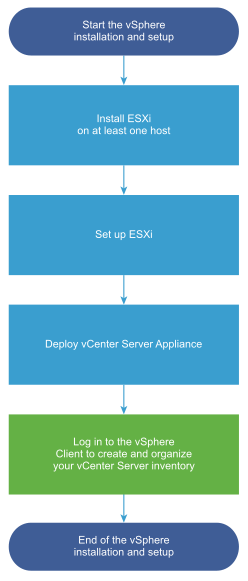
In my previous two posts we already finished the above first two steps with Install ESXi on at least one host and Set up ESXi.
Below we will now move on with Deploy vCenter Server Appliance to accomplish finally our vSphere environment in our on-premise data center.
Deploy vCenter Server Appliance
VMware has deprecated vCenter Server for Windows with the release of vSphere 6.7. The next version of vSphere (not update release) will not include vCenter Server for Windows (vSphere 6.7 Release Notes).
Why Is VMware deprecating vCenter Server for Windows?
VMware is consistently striving to simplify data center administration and lifecycle management for IT. One way to achieve this goal is by simplifying the deployment of vCenter Server, the centralized management platform for vSphere environments.
The vCenter Server Appliance (VCSA) was first introduced with the release of vSphere 5.0 and has since evolved to become the definitive deployment model for vCenter Server. For a while now, VMware has been publicizing the benefits of the appliance deployment model over its Windows counterpart. With vSphere 6.5 and subsequently vSphere 6.5 Update 1, the VCSA has become the fundamental building block of a vSphere environment.
Source: https://blogs.vmware.com/vsphere/2017/08/farewell-vcenter-server-windows.html
Introduction about the vCenter Server Appliance
You can deploy the vCenter Server appliance on an ESXi host 6.5 or later.
When you use Fully Qualified Domain Names, verify that the client machine from which you are deploying the appliance and the network on which you are deploying the appliance use the same DNS server.
Before you deploy the appliance, synchronize the clocks of the target server and all vCenter Server instances on the vSphere network. Unsynchronized clocks might result in authentication problems and can cause the installation to fail or prevent the appliance services from starting. See Synchronizing Clocks on the vSphere Network.
The vCenter Server appliance package contains the following software:
- Photon OS® 3.0
- The vSphere authentication services
- PostgreSQL
- VMware vSphere Lifecycle Manager Extension
- VMware vCenter Lifecycle Manager
For the set up and deployment I will refer to the following documentation from NVIDIA in order to set up the vCenter Server Appliance (VCSA).
Installing VMware vCenter Server
https://docs.nvidia.com/ai-enterprise/deployment-guide-vmware/0.1.0/vcenter.html
The VCSA is a preconfigured virtual appliance built on Project Photon OS that allows you to manage multiple ESXi hosts and perform configuration changes from a single pane of glass. Since the OS was developed by VMware and accelerated by NVIDIA vGPUs, it offers better performance and boot times than the previous Linux-based appliance. Furthermore, it uses an embedded vPostgres database, giving VMware complete control of the software stack in tandem with the performance of NVIDIA-certified Systems. This results in significant optimization for vSphere environments and quicker release of security patches and bug fixes, enabling IT admins to focus on organizational goals and strategic initiatives.
The VCSA scales up to 2500 hosts and 45,000 virtual machines. Features such as Update Manager are bundled into the VCSA, file-based backup and restore, and vCenter High Availability. The appliance also saves operating system license costs and is quicker and easier to deploy and patch.
vCenter Server Appliance (VCSA) Installation
I will use for this post a free trial version of the VMware vCenter Server Appliance version 8.0U2a.
The VMware vCenter Server Appliance ISO includes the UI and CLI installer for install, upgrade and migration for VMware vCenter Server Appliance, VMware vSphere Update Manager and Update Manager Download Service (UMDS).
Download under https://customerconnect.vmware.com/en/evalcenter?p=vsphere-eval-8
Mount the ISO on your computer. The VCSA installer is compatible with Mac, Linux, and Windows.
I will run the installer from a client computer (Windows 10) which is a member in the domain. Finally the OS you will use to deploy VCSA needs network access to your ESXi host on which you want to deploy this preconfigured virtual appliance (virtual machine based on the Photon OS).
Photon OS, is an open-source minimalist Linux operating system from VMware that is optimized for cloud computing platforms, VMware vSphere deployments, and applications native to the cloud.
Source: https://vmware.github.io/photon/assets/files/html/3.0/Introduction.html
You can use the GUI method to deploy the appliance interactively. Alternatively, you can use the CLI method to perform a silent deployment of the appliance. I will use below the GUI.
As we are installing a new instance, click Install.
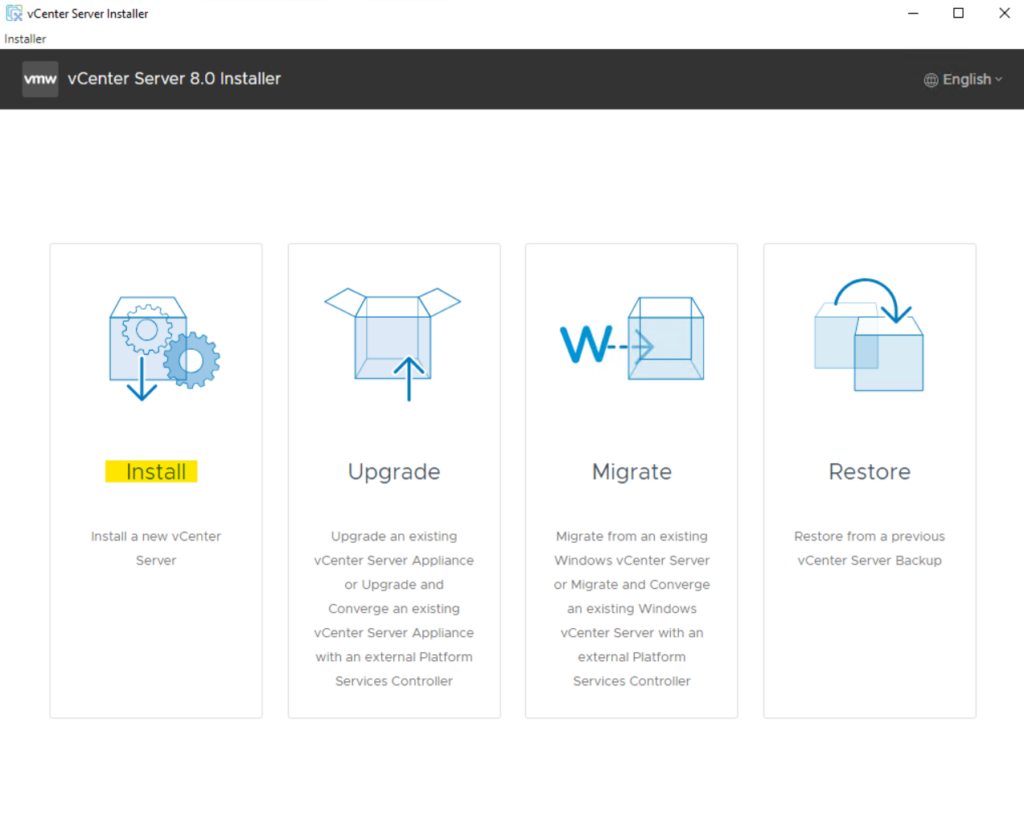
The install is two stages. We begin with Stage1: Deploy vCenter Server. Click Next to start.
Read and accept the EULA, and then click Next to continue.
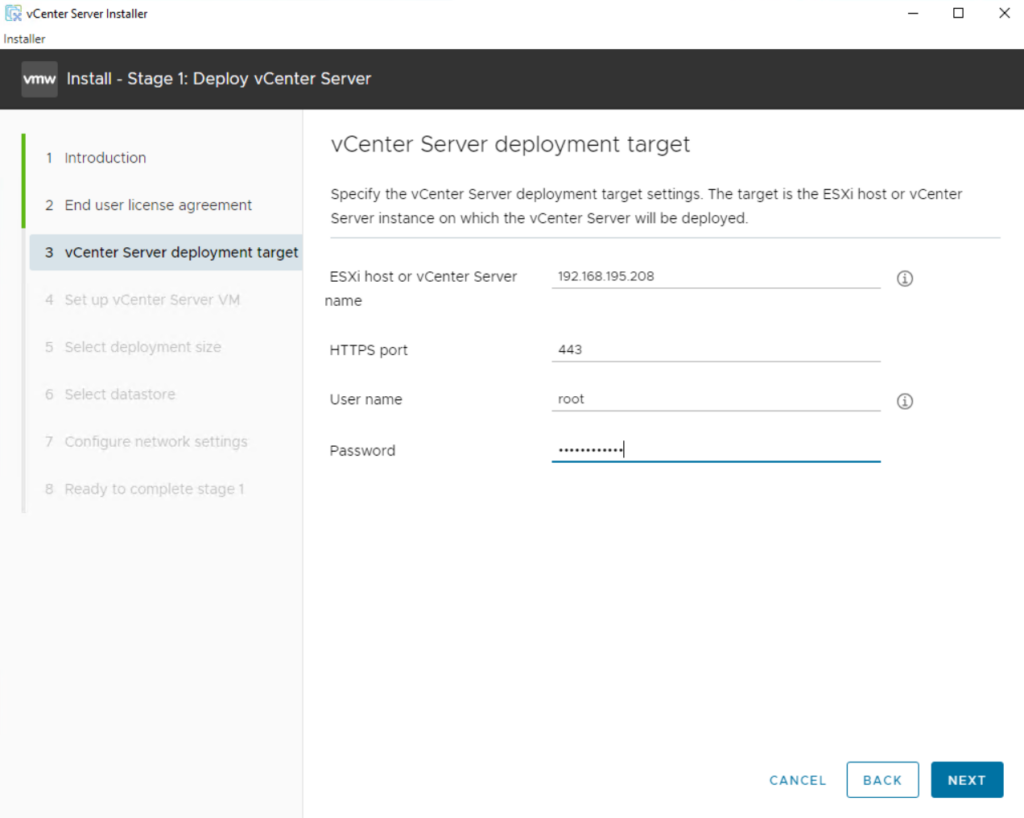
Select the ESXi host on which to install the VCSA (vCenter Server Appliance) as a guest. This must be a host that runs ESXi 6.5 or later.
NVIDIA recommends that the vCenter server (Windows or appliance-based) run on a separate management cluster from the one designated for VDI workloads. Enter the IP address or fully qualified domain name (FQDN) of the chosen host, its root username, and password; then click Next.
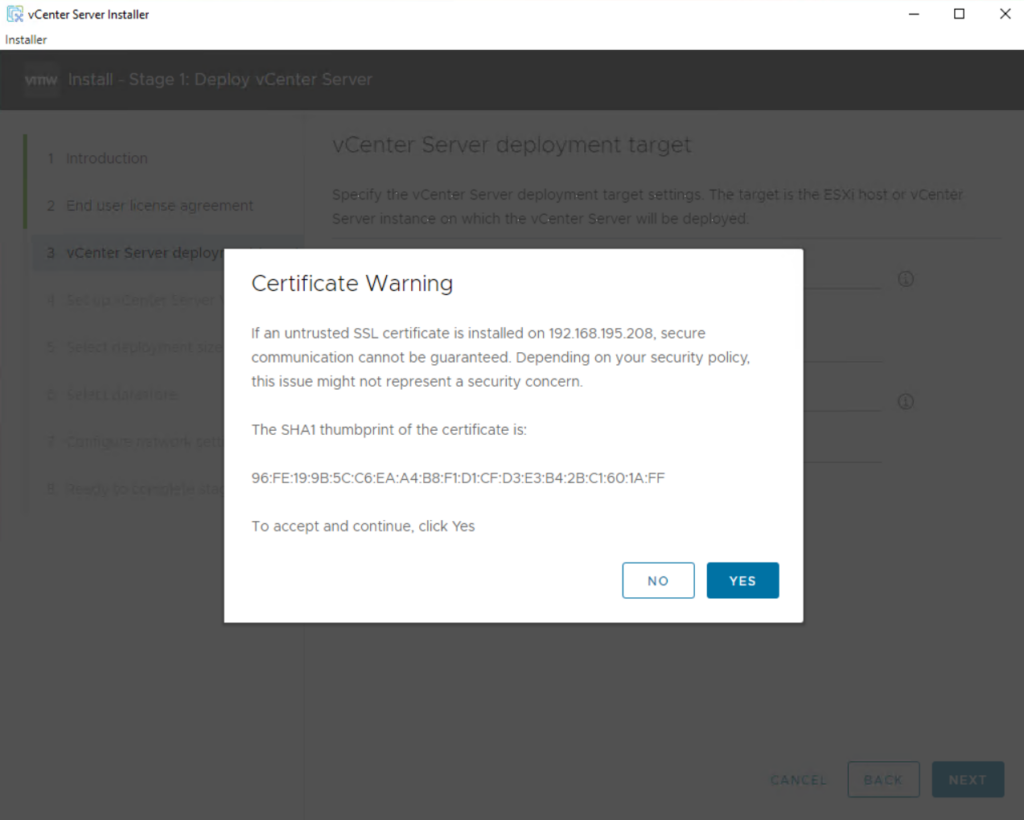
If your desktop can reach the host, you should see a certificate warning as it connects. This warning is due to the use of a self-signed certificate. If you are using a signed certificate, you will not see this warning. Click Yes to continue.
The credentials are validated.
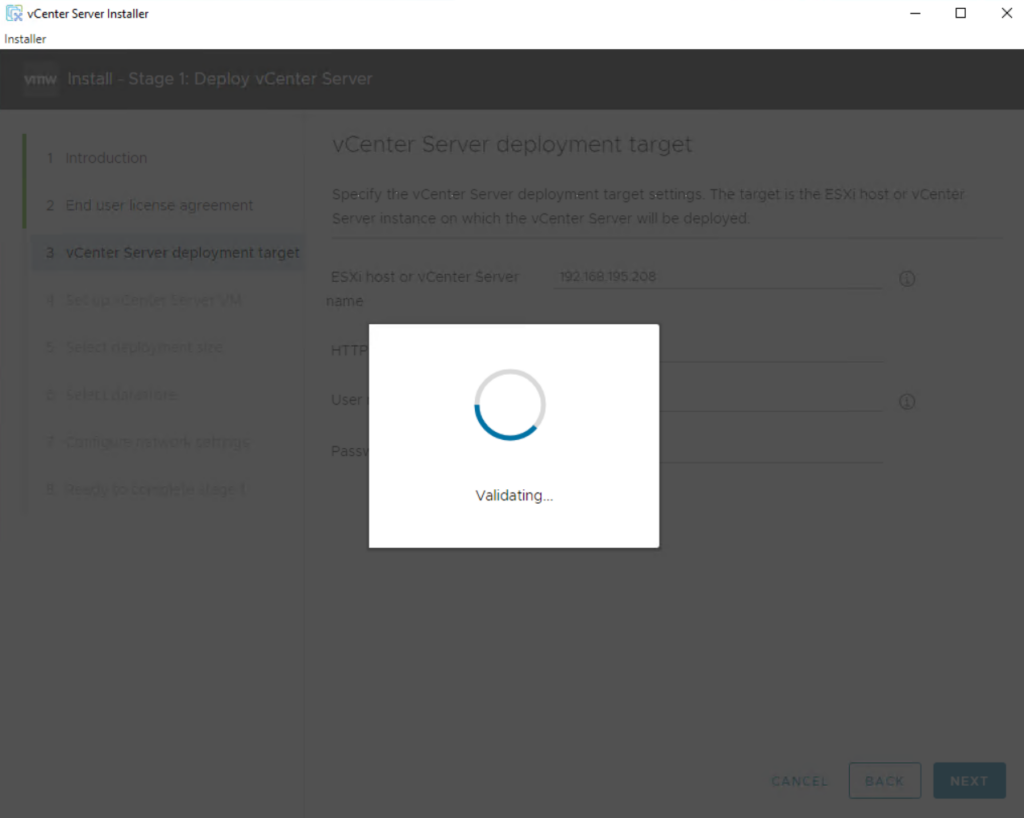
When prompted after a successful connection, provide a VM name for the vCenter Server 8, type the passwords in the Set Root password field, and enter the root password again, and click Next.
In case we lost this password, we can reset it by using the GRUB 2 Boot Loader as for usual Linux operating systems and shown in my following post https://blog.matrixpost.net/how-to-reset-forgotten-or-not-knowing-root-password-for-linux-by-using-the-grub-boot-loader/.
When the VMware Photon OS (vCenter appliance) is booting, press the E key as far as the Photon OS GUI boot screen appears and follow the steps shown in my post.
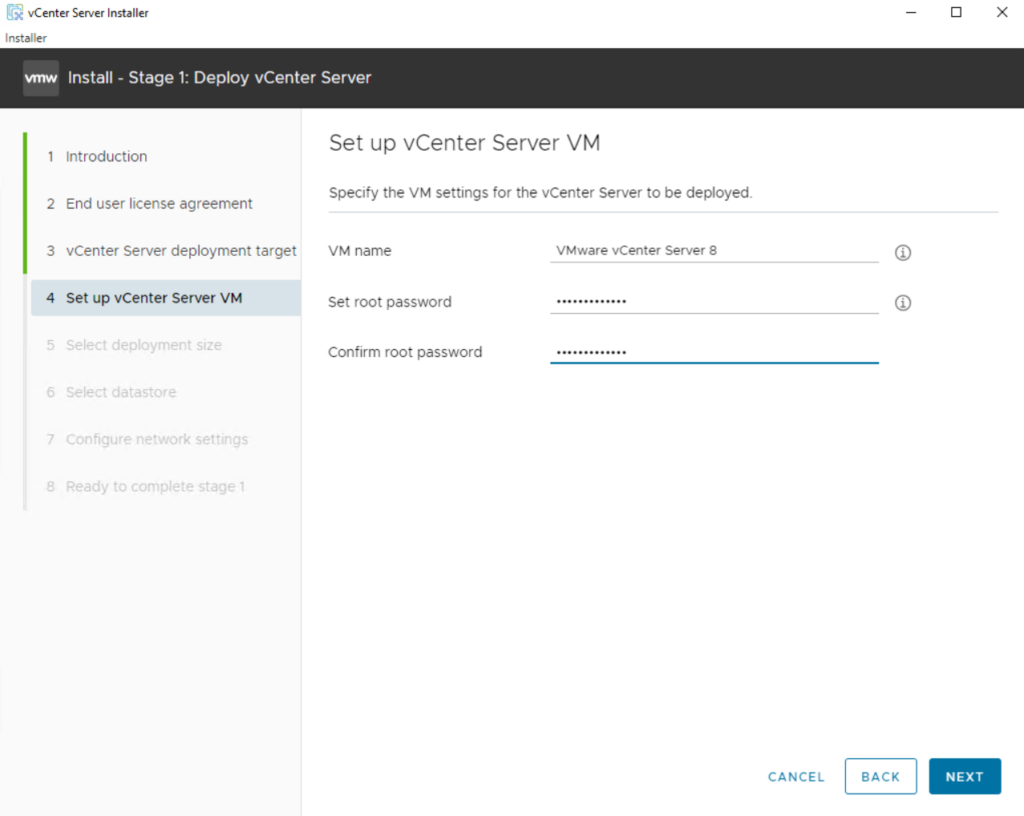
Select a deployment size appropriate to the number of hosts and virtual machines that vCenter Server will manage, then click Next.
The option that you select determines the number of CPUs and the amount of memory for the appliance. The hardware requirements for a vCenter Server appliance depend on the size of your vSphere inventory.
Because I will have just one ESXi host (256 GB RAM) in my network for evaluation purpose, I will not have more than 100 VMs on this host and therefore I will use by default Tiny for the deployment size.
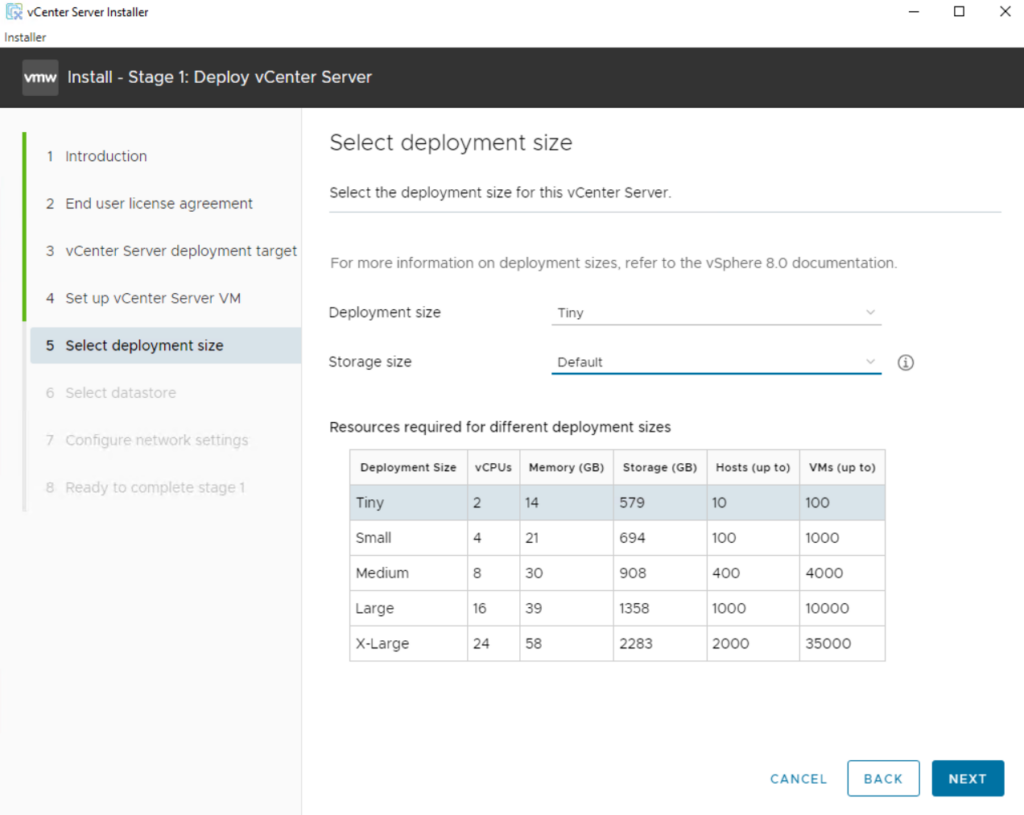
Select the datastore where the VCSA will be deployed, select thin provisioning if required, and click Next
A thin provisioned disk does not pre-allocate all of the space specified for the disk (like e.g. a VHDX dynamically expanding virtual hard disk in Microsoft Hyper-V). It saves space by allocating only blocks backed by physical storage when they are written. NFS datastores are thin provisioned by default.
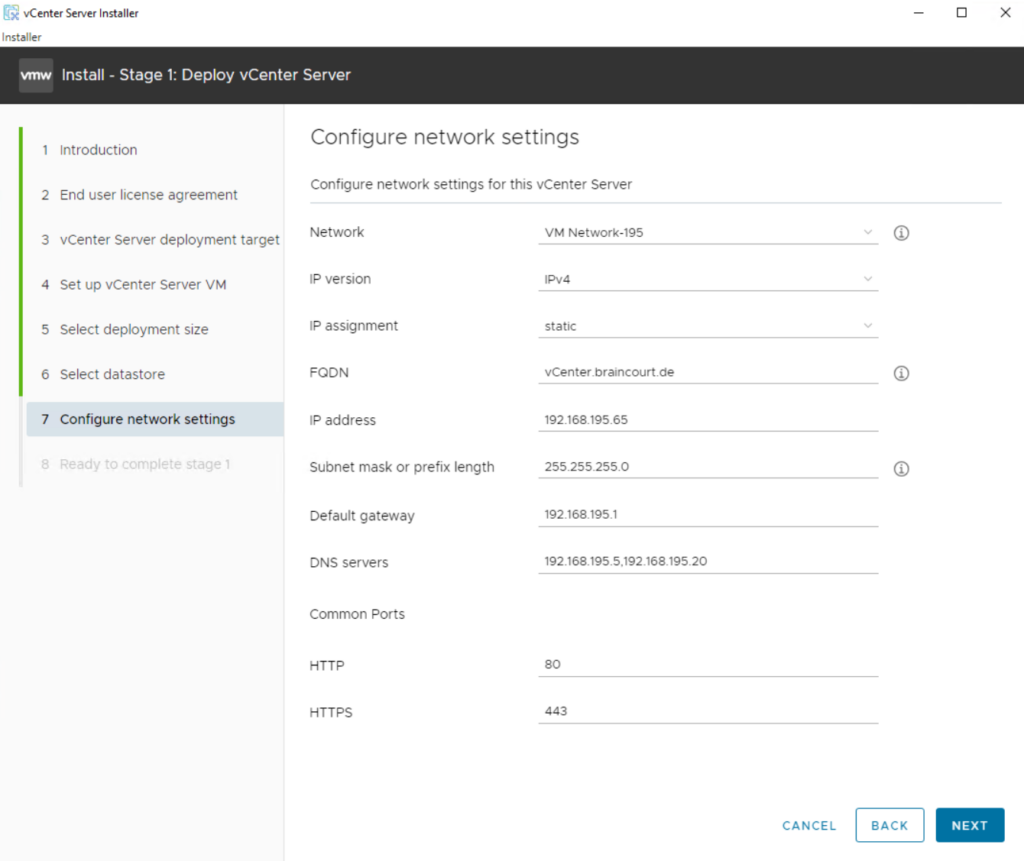
The installer displays the Configure network settings. Before you configure these settings, choose an appropriate static IP address, and enter it into local DNS (e.g., on the Domain Controller). Once you can resolve the address, enter the IP address hostname on the network setting page, then scroll down and enter the remaining items. When all desired settings are complete, select Next.
When ESXi is used as the deployment target, non-ephemeral distributed virtual portgroups are not supported and hence, not shown in the Network dropdown list.
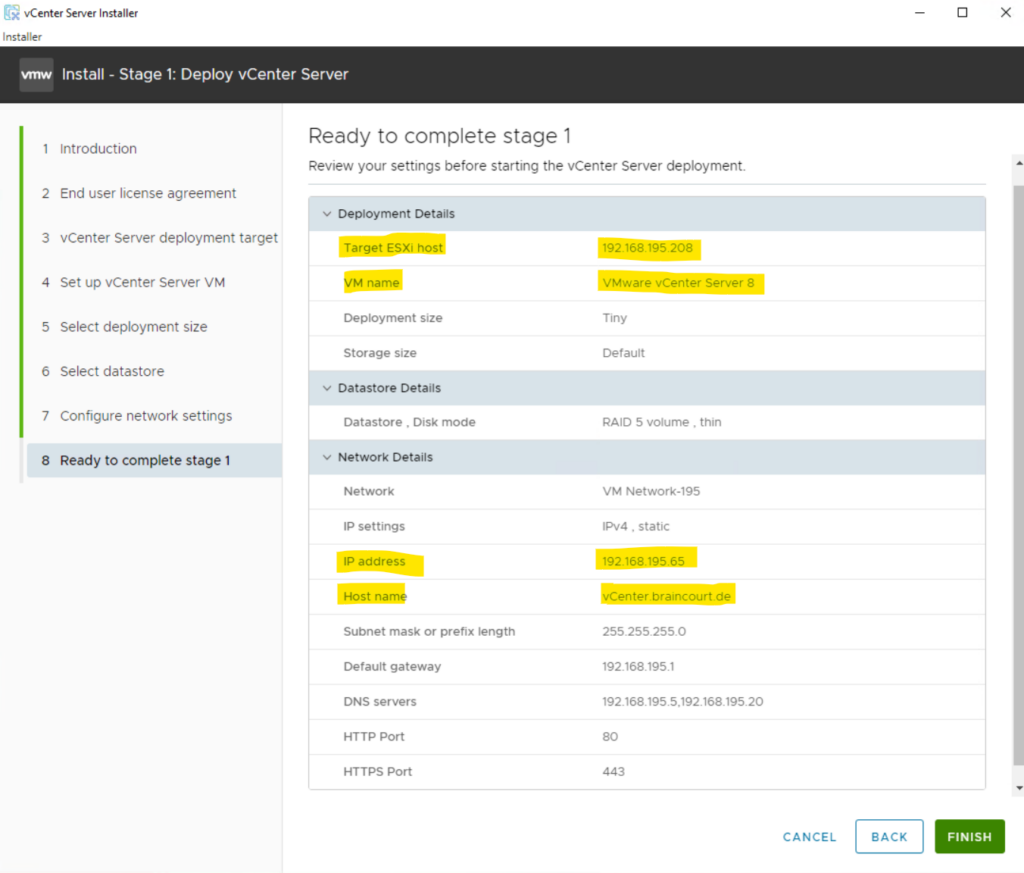
Review the settings before starting the vCenter Server deployment and click Finish to start the installation.
The vCenter Server will start deploying on the specified target ESXi host. Installation progress can be viewed on the screen
With the VCSA now deployed, move on to stage 2 by clicking Continue.
If you exit, you can continue with the vCenter Server setup at any time by logging in to the vCenter Server Management Interface https://vCenter.braincourt.de:5480/
Select Next to proceed with Stage 2, setting up the vCenter Server.
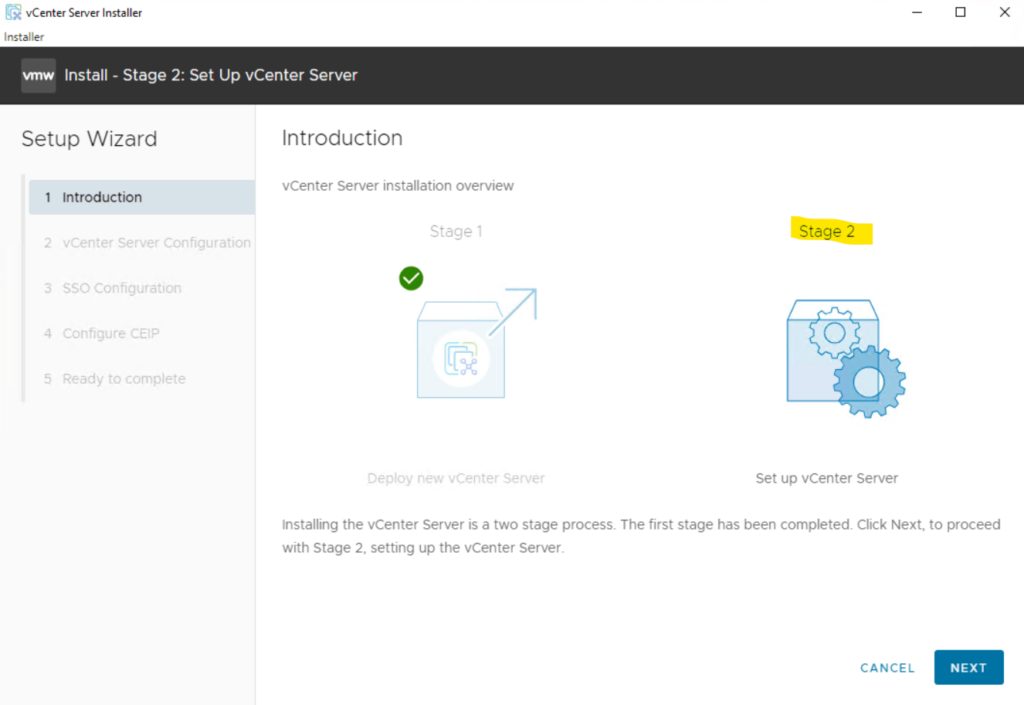
Configure the NTP server by selecting the Time synchronization mode and Enabling the SSH access, then click Next
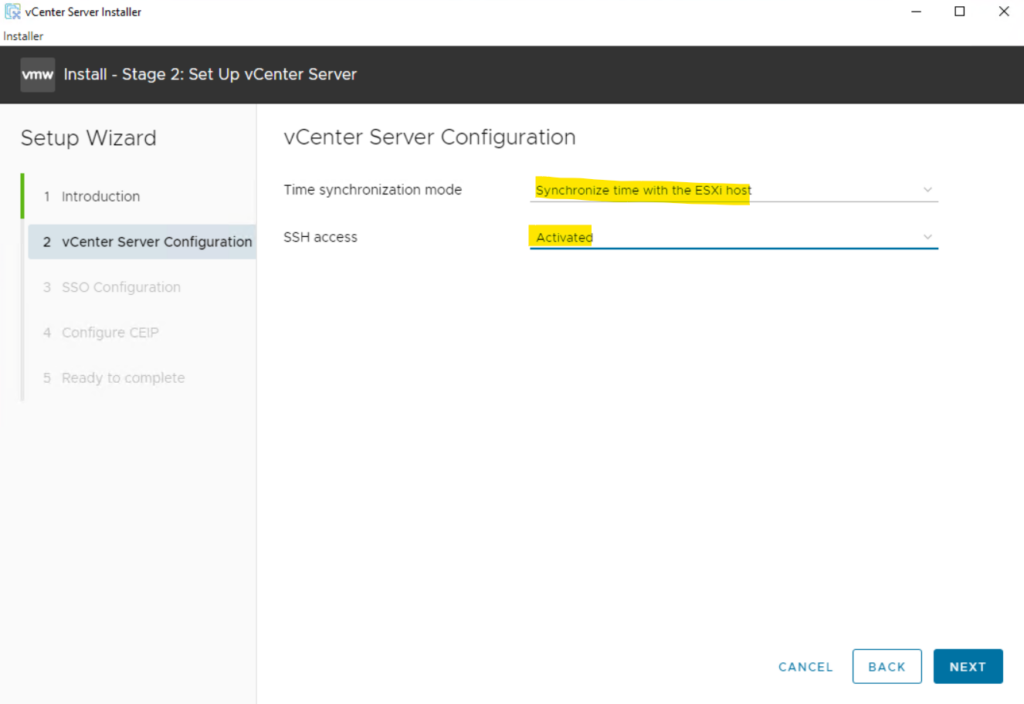
Enter a unique SSO domain name, configure a password for the SSO administrator, click Next.
Note !
The default SSO domain name is vSphere.local.
The SSO domain name should not be the same as your Active Directory Domain.
Just for demonstration purpose I will use here the default SSO domain name.
After installation, the administrator of the vCenter Single Sign-On domain, administrator@vsphere.local by default, has administrator access to both vCenter Single Sign-On and vCenter Server. That user can then add identity sources, set the default identity source, and manage users and groups in the vCenter Single Sign-On domain.
Select or deselect the customer experience improvement program box and click Next.
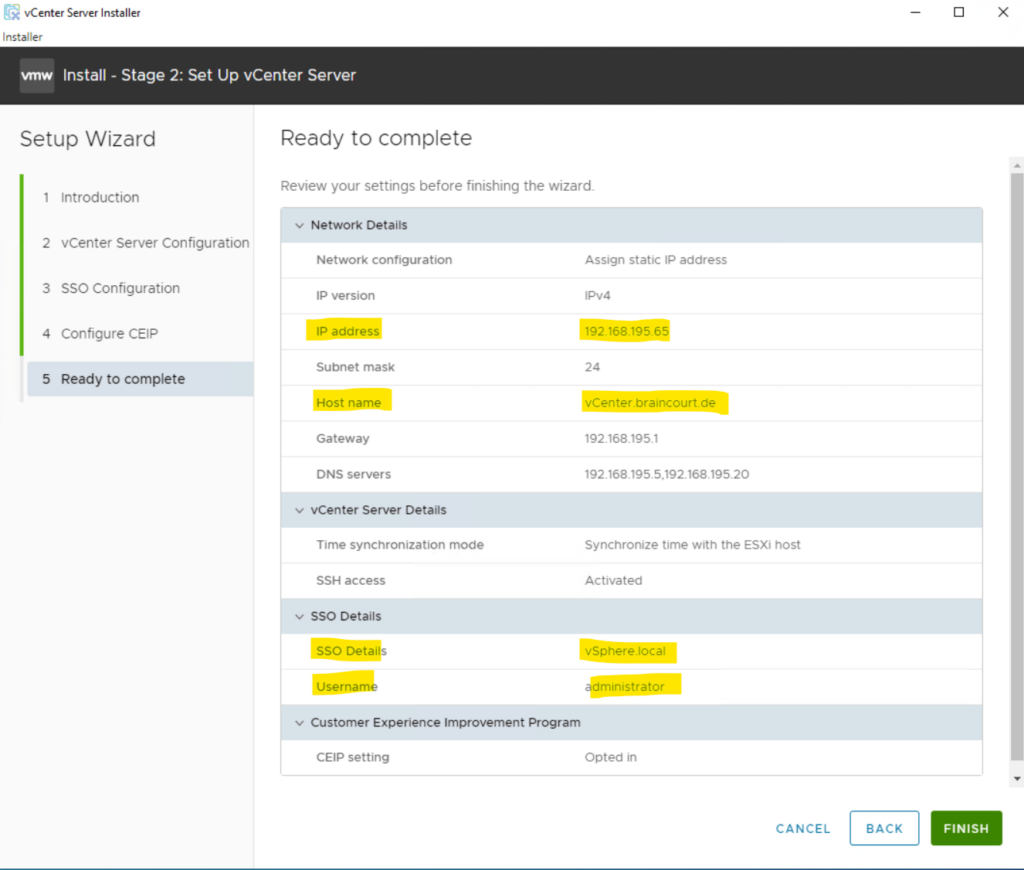
Review the details on the summary page and click Finish to finalize the setup.
The installer displays a warning that you cannot pause or stop the install once you start it. Click Ok to acknowledge the warning and start the install.
When the install process is complete, click Close to exit the installer and entire Stage 2 of the VCSA setup.
vCenter Server Getting Started Page : https://vCenter.braincourt.de:443
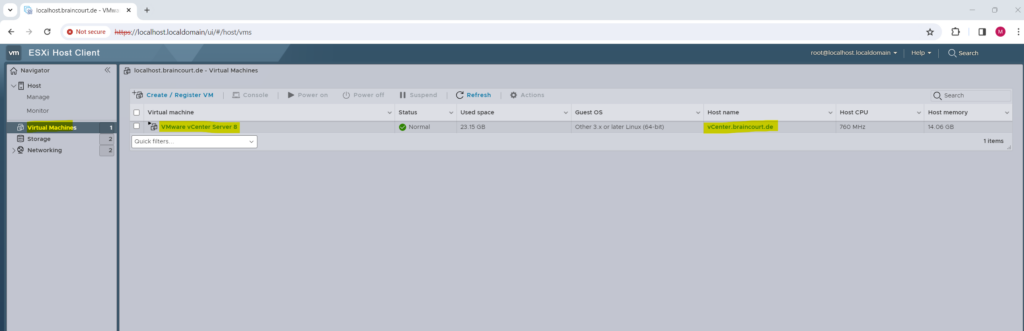
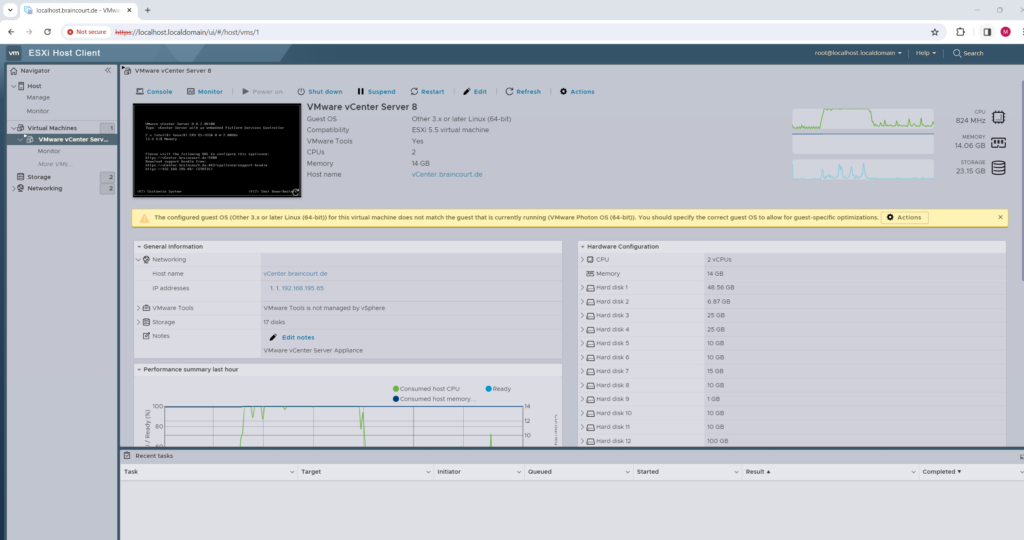
The VCSA virtual machine we deployed we will see already within the ESXi Host Client (ESXi Web UI).
So far we finished within the vSphere Installation and Setup Workflow the step Deploy vCenter Server Appliance as shown below.
vSphere Installation and Setup Workflow
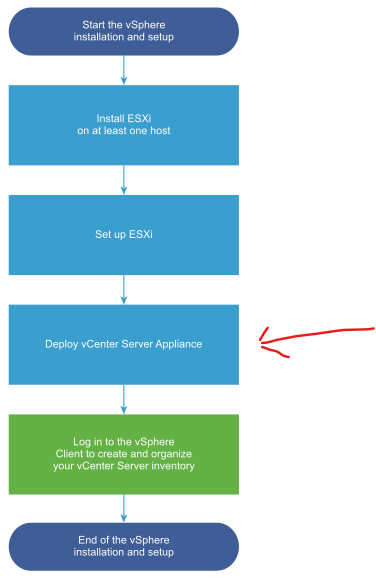
The last step is to configure the vCenter server (appliance) which I will show in part 2.
Links
VMware vSphere Bitfusion Documentation
https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-vSphere-Bitfusion/index.htmlWhat’s New in vSphere 8?
https://core.vmware.com/resource/whats-new-vsphere-8vSphere Permissions and User Management Tasks
https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-vSphere/7.0/com.vmware.vsphere.security.doc/GUID-5372F580-5C23-4E9C-8A4E-EF1B4DD9033E.htmlWhat is Cloud Architecture?
https://www.vmware.com/topics/glossary/content/cloud-architecture.htmlvSphere Support and Learning
https://kb.vmware.com/s/vsphereGetting Started with Datacenter CLI
https://blogs.vmware.com/vsphere/2016/12/getting-started-datacenter-cli.htmlOverview of vSphere Command-Line Interfaces
https://vdc-repo.vmware.com/vmwb-repository/dcr-public/bc4fa31a-40ac-4aa9-a6a1-7171d1fff7f4/740990ee-4d65-4627-a9d4-0f046cb78aec/doc/GUID-24E7EEFC-08F1-451C-850C-5F158322BAC9.htmlWhat is VMware vSphere Bitfusion?
https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-vSphere-Bitfusion/index.htmlWhat is VMWare vSphere Replication?
https://docs.vmware.com/en/vSphere-Replication/index.htmlSRM – Array Based Replication vs. vSphere Replication
https://blogs.vmware.com/virtualblocks/2017/06/22/srm-array-based-replication-vs-vsphere-replication/
Follow me on LinkedIn


